The Evolution of Brain-Inspired Computer Vision

The Evolution of Brain-Inspired Computer Vision
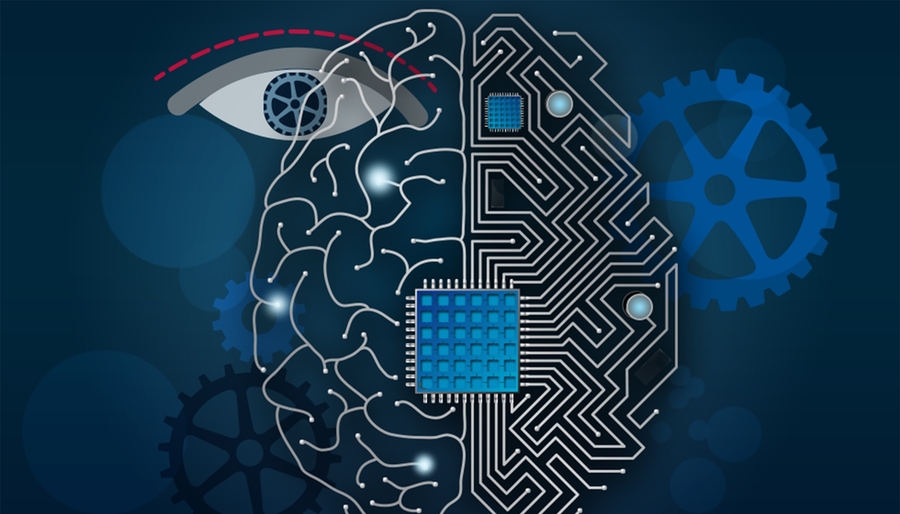
Do we know AI? By many sectors, serious leaps forward have been made artefacts having turned into clever helpers with recent progress marked by the fact that machines can be taught to “see” much like we do. Brain-Inspired Computer Vision is at the forefront of this evolution. I want to talk about this, how computers are trained to look at stuff just like our brains do, but even cooler.
Understanding the Basics of Computer Vision
We must learn the basics! Though built on complex algorithms and set rules to spot patterns and things in photos, traditional computer vision systems might have trouble when the scenes become too tricky; thus, by taking cues from the human brain; we’re trying to improve this technology even further.
Challenges in Conventional Computer Vision
I see problems; computers can get confused. Things like blocked objects, changing light, and weird shiny things – they are not easily noticed or known by computers – cause mistakes when a simple computer tries to see like we do. Can I get it to work like the human eye?
The Paradigm Shift
I study computer vision. Computer-enabled sight skills have grown because brain-like methods were studied, but has this made computers see better because the human brain was copied in smart robots and software? We look into making computers see like we do.
The Building Blocks of Human-Like Vision
Central to the brain-inspired approach is the utilization of neural networks. These are computational models designed to replicate the interconnected structure of neurons in the human brain. By leveraging neural networks, AI systems can process and analyze visual information in a manner closely resembling human cognition.
Synaptic Plasticity
In the human brain, synaptic plasticity allows for the adaptation and learning from visual stimuli. Incorporating this concept into AI systems enhances their ability to adapt to diverse and evolving visual environments. The dynamic nature of synaptic connections enables machines to learn and improve their recognition capabilities over time.
Hierarchical Processing
We see; we think; we learn.
By the parts of the eye’s path in our brains— much like steps on a ladder— basic to more bits of things we look at are gazed upon by us one by one; squinting at simple dots evolves into making out shapes until – goodness! – the big picture is quietly made clear to all of us.
As we understand the world around us, vision happens in stages; each more complex than the last.
Sensory Integration
I see; hear; touch. The broad look we have at everything around us isn’t just because we can see well – it’s learned from hearing and feeling too, all mixed together by our brains. We take in sights, sounds, and textures—and that amazing blend helps us figure stuff out from every angle. Our brain helps us to make sense of the world with a rich mix of insights and feelings, just like people do!
Learning from Experience
I study. AI is smartened beyond just memorizing things; it is made to learn from trying, getting better as it practices, with something called reinforcement learning helping a lot; this is kind of like how kids get smarter by messing up and then trying again. So, we see computers getting sharper, thanks to the way they now learn; kind of like how we learn each day, figuring things out a bit better every time.
Real-World Applications
Can we be smarter? When a brain-like strategy for computer vision is used; it has a big effect on lots of jobs; like when AI checks health pictures, it spots sickness early, being very exact. In cars that drive themselves, this tech gives them human smarts to move safely and quickly through lots of cars and buses; and don’t forget trucks. I think it’s awesome; it’s like computers can almost think; it can really change things!
Overcoming Ethical Considerations
As we venture into the realm of enhancing computer vision through a brain-inspired approach, it is imperative to address ethical considerations, including AI’s role in image recognition and generation. Responsible AI development involves ensuring transparency, accountability, and unbiased decision-making. Striking a balance between technological innovation and ethical principles is essential to harness the full potential of this transformative approach.
Conclusion
The journey towards “Enhancing Computer Vision: A Brain-Inspired Approach for Human-Like Perception” marks a paradigm shift in the field of AI. The integration of neural networks, synaptic plasticity, hierarchical processing, sensory integration, and reinforcement learning propels computer vision towards a level of sophistication that mirrors the intricacies of human perception. As we navigate this frontier, it is crucial to priorities responsible AI development, ensuring that these advancements benefit society ethically and sustainably. The future holds promising possibilities as we strive to bridge the gap between artificial and human vision.